What Do the MBTI Letters Stand For?
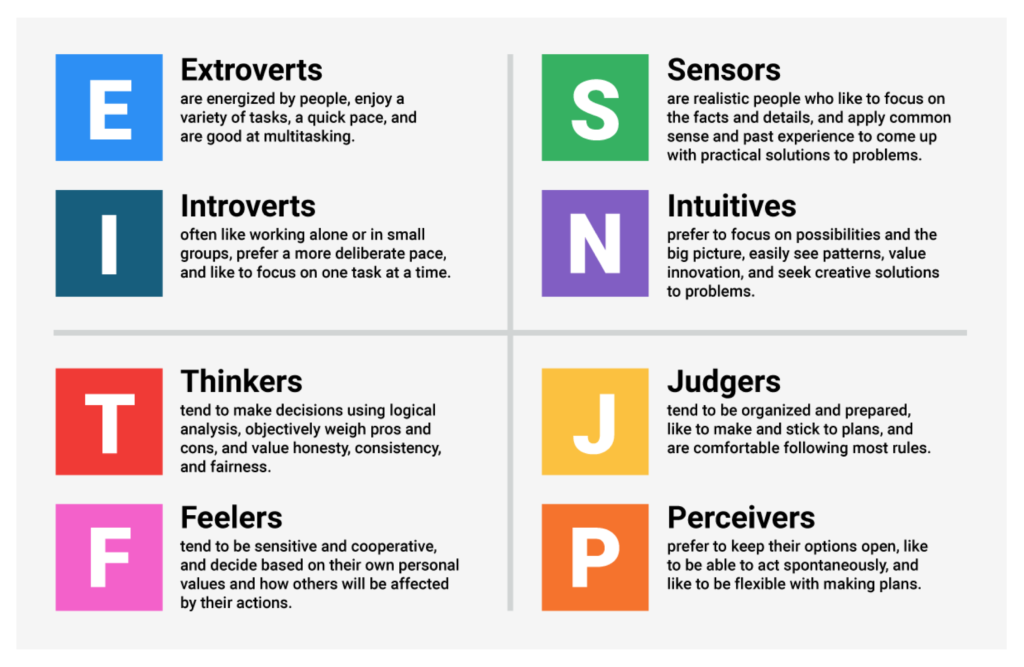
Table of Contents
The world of psychology is a vast landscape, full of theories and frameworks aimed at unraveling the mysteries of human personality. Among these, the Myers-Briggs Type Indicator (MBTI) stands as a beacon, guiding us through the intricate maze of individual differences. But what exactly do those four enigmatic letters in your MBTI type signify, and how can they help us understand ourselves and others better? In this comprehensive guide, we embark on a journey to demystify the MBTI, examining each letter in detail and addressing common questions that arise about this fascinating personality tool.
What Does MBTI Stand For?
Let's begin with the basics. MBTI stands for "Myers-Briggs Type Indicator." It is a widely recognized and respected psychological assessment tool developed by Katharine Cook Briggs and her daughter Isabel Briggs Myers. This instrument is designed to provide insights into an individual's personality, preferences, and the ways they interact with the world.
Breaking Down the Four MBTI Letters
At the heart of the MBTI lie four letters, each representing a unique dimension of personality. These letters, when combined, result in one of 16 possible personality types. Let's explore each letter's meaning and significance:
Extraversion (E) vs. Introversion (I)
The first letter of your MBTI type indicates whether you lean more toward extraversion (E) or introversion (I). This dimension revolves around your social orientation and the source of your energy.
- Extraversion (E): Extraverts thrive in social settings. They gain energy from external stimuli and interactions with others. Extraverts are often expressive, outgoing, and enthusiastic. They are the life of the party, the chatterbox at the office, and the ones who make friends easily.
- Introversion (I): Introverts, on the other hand, find their energy drained by excessive socializing. They value solitude and introspection, often preferring one-on-one interactions or smaller, more intimate gatherings. Introverts are known for their deep thinking, reflective nature, and ability to concentrate deeply on tasks.
Understanding the "E" or "I" in your MBTI type provides insights into how you recharge and engage with the world, influencing your social interactions, communication style, and the environments where you thrive.
Sensing (S) vs. Intuition (N)
The second letter of your MBTI type indicates whether you tend to lean toward sensing (S) or intuition (N), which shapes how you perceive and process information.
- Sensing (S): Sensors are grounded in the here and now. They rely on their five senses to gather concrete, tangible information from the physical world. Sensors are detail-oriented, practical, and observant of their surroundings. They excel at handling facts, data, and specifics.
- Intuition (N): Intuitives are drawn to the abstract and the possibilities that lie beyond the immediate. They have a knack for spotting patterns, connecting dots, and envisioning future scenarios. Intuitives are imaginative, visionary, and comfortable with ambiguity. They often trust their gut feelings and hunches.
The "S" or "N" in your MBTI type determines how you take in the world, influencing your learning style, problem-solving approach, and the way you process information to make decisions.
Thinking (T) vs. Feeling (F)
The third letter of your MBTI type indicates whether you tend to make decisions using thinking (T) or feeling (F). This dimension highlights your decision-making process and how you evaluate information.
- Thinking (T): Thinkers are logical and analytical in their decision-making. They prioritize objectivity, rationality, and consistency. Thinkers are adept at assessing situations based on facts, rules, and cause-and-effect relationships. They value fairness and often seek to find the most reasonable solution.
- Feeling (F): Feelers, in contrast, prioritize empathy, harmony, and the impact of decisions on people's feelings. They make choices based on personal values, emotions, and consideration of others' needs. Feelers excel in situations that require interpersonal sensitivity and empathy.
The "T" or "F" in your MBTI type shapes your approach to decision-making, conflict resolution, and how you navigate ethical dilemmas.
Judging (J) vs. Perceiving (P)
The fourth and final letter of your MBTI type determines whether you have a preference for judging (J) or perceiving (P), which relates to how you interact with the external world and manage your time.
- Judging (J): Judgers appreciate structure and organization. They tend to plan ahead, set goals, and prefer closure. Judgers thrive in orderly environments, make to-do lists, and take a systematic approach to tasks. They enjoy completing projects and sticking to schedules.
- Perceiving (P): Perceivers are flexible and adaptable. They're open to new information and like to keep their options open. Perceivers are spontaneous, often making decisions on the fly. They enjoy exploring possibilities, embracing change, and going with the flow.
The "J" or "P" in your MBTI type offers insights into your time management, planning style, and how you handle uncertainty and spontaneity in your life.
 Shams Hoque
Shams Hoque

u/Artistic_Anteater_91
Sep 03, 2023 11:41 pmu/Nerwene
Sep 04, 2023 01:21 amI vs E: Your dominant function is either introverted (I) or extraverted (E).
N vs S: Your dominant or auxiliary function is either intuition (Ne, Ni) or sensing (Se, Si).
T vs F: Your dominant or auxiliary function is either thinking (Te, Ti) or feeling (Fe, Fi).
J vs P: If the first extraverted function of the stack is a judging one, then xxxJ type. If it's a perceiving one, xxxP type. Remember that J functions = Thinking and Feeling. P functions = Sensing and Intuition.
Let's take the stack Fi-Se-Ni-Te as an example.
Fi is an introverted feeling function and it's in the dominant position. So we have an IXFX type.
Se as an auxiliary = ISFX type.
The first extraverted function of the stack is Se, which is a perceiving function. = ISFP.
Let's take the stack Te-Ni-Se-Fi as an example.
Te is an extraverted thinking function and it's in the dominant position. So we have an EXTX type.
Ni as an auxiliary = ENTX type.
The first extraverted function of the stack is Te, which is a judging function. = ENTJ.